Human Depth Sensors-Based Activity Recognition Using Spatiotemporal Features and Hidden Markov Model for Smart Environments
Duration
[2014 – 2016], Designation = Research Associate
Supported by
The research was supported by the Implementation of Technologies for Identification, Behavior, and Location of Human Based on Sensor Network Fusion Program through the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (Grant no. 10041629). This work was supported by Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (B0101-16-0552, Development of Predictive Visual Intelligence Technology).
Project Description
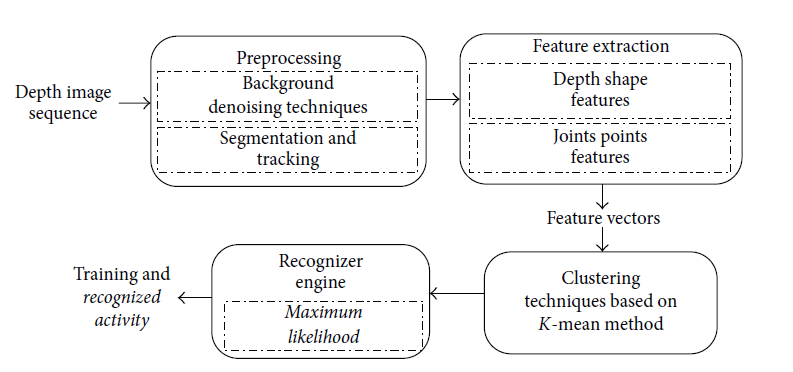
Nowadays, advancements in depth imaging technologies have made human activity recognition (HAR) reliable without attaching optical markers or any other motion sensors to human body parts. This study presents a depth imaging-based HAR system to monitor and recognize human activities. In this work, we proposed spatiotemporal features approach to detect, track, and recognize human silhouettes using a sequence of RGB-D images. Under our proposed HAR framework, the required procedure includes detection of human depth silhouettes from the raw depth image sequence, removing background noise, and tracking of human silhouettes using frame differentiation constraints of human motion information. These depth silhouettes extract the spatiotemporal features based on depth sequential history, motion identification, optical flow, and joints information. Then, these features are processed by principal component analysis for dimension reduction and better feature representation. Finally, these optimal features are trained and they recognized activity using hidden Markov model. During experimental results, we demonstrate our proposed approach on three challenging depth videos datasets including IM-Daily Depth Activity, MSRAction3D, and MSRDailyActivity3D. All experimental results show the superiority of the proposed approach over the state-of-the-art methods.