Wearable Sensor-Based Human Behavior Understanding and Recognition in Daily Life for Smart Enviroments
Duration
[2018 – 2018]
Supported by
This research is supported by the Basic Research Business, Dubai, under the “Innovative Ecosystem Development Scheme” (Grant No. GRSUP32830) cooperated with the DITH (Digital Information and Tele-health Department).
Project Description
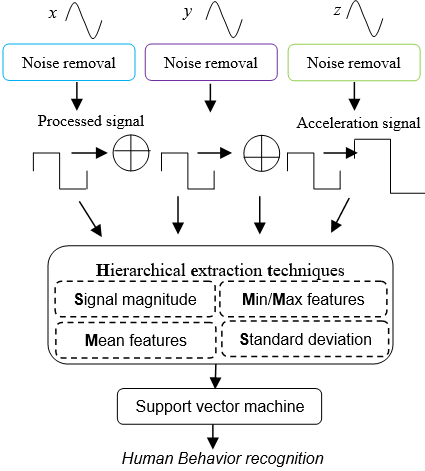
Human behavior recognition driven by motion sensors have gained significant research importance in e-healthcare and life-log analysis systems, especially for daily routine monitoring and improving quality of life. The anatomy of human behaviors have long been under-study using wearable sensors in a smart environment which recognize behaviors in a free-living environment. This paper proposed a novel scheme for the recognition of different human behaviors using wearable sensors i.e. triaxial accelerometer. To ensure robust performance of the proposed model, hierarchical features are used. These features include signal magnitude, positive/negative peaks and position direction to explore signal orientation changes, position differentiation, temporal variation and optimal change among coordinates. In addition, these features are processed by the dynamics of their respective class to learned, symbolized, trained and recognized using linear support vector machine. Experimental results showed that the proposed feature extraction strategy outperformed over the others. The proposed system should be used as recommender system based on behavioral pattern of pedestrian at road, players in sports, children at school and patients of Parkinson disease.