A Novel Statistical Method for Scene Classification Based on Multi-Object Categorization and Logistic Regression
Duration
[2019 – 2020], Designation = Research Associate
Supported by
This research was partially supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (no. 2018R1D1A1A02085645). Also, it was supported by a grant (19CTAPC152247-01) from Technology Advancement Research Program funded by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korean government.
Project Description
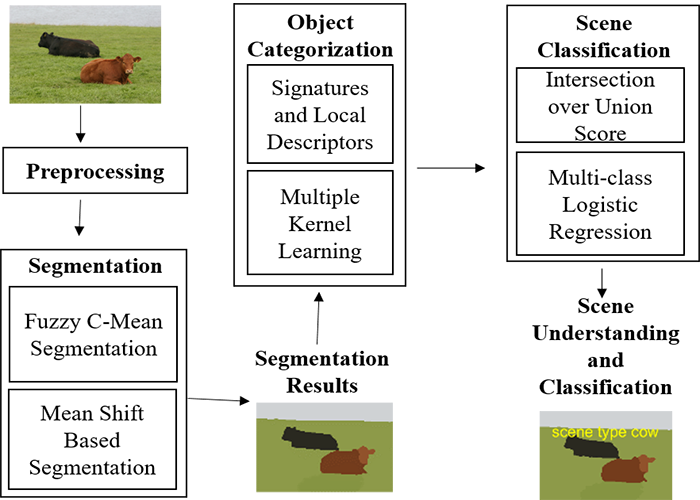
In recent years, interest in scene classification of different indoor-outdoor scene images has increased due to major developments in visual sensor techniques. Scene classification has been demonstrated to be an efficient method for environmental observations but it is a challenging task considering the complexity of multiple objects in scenery images. These images include a combination of different properties and objects i.e., (color, text, and regions) and they are classified on the basis of optimal features. In this project, an efficient multiclass objects categorization method is proposed for the indoor-outdoor scene classification of scenery images using benchmark datasets. We illustrate two improved methods, fuzzy c-mean and mean shift algorithms, which infer multiple object segmentation in complex images. Multiple object categorization is achieved through multiple kernel learning (MKL), which considers local descriptors and signatures of regions. The relations between multiple objects are then examined by intersection over union algorithm. Finally, scene classification is achieved by using Multi-class Logistic Regression (McLR). Experimental evaluation demonstrated that our scene classification method is superior compared to other conventional methods, especially when dealing with complex images. Our system should be applicable in various domains such as drone targeting, autonomous driving, G lobal positioning systems, robotics and tourist guide applications.